Pigshell
unix the web
Pigshell is a pure client-side Javascript app running in the browser, which presents resources on the web as files. These include public web pages as well as private data in Google Drive, Dropbox, Facebook and even your desktop. It provides a command line interface to construct pipelines of simple commands to transform, display and copy data.
Pigshell is free software, released under the GNU GPLv3.
Pigshell is inspired by Unix philosophy: Everything is a file. Programs should do one thing well. Create tools by stringing together a combination of simpler tools. Like human language, CLIs give us freedom of expression - we can generate infinite meaningful combinations from a limited number of words to effectively deal with the combinatorial explosion of variety thrown up by the modern web environment.
We're far from done, but here are some of the things you can do right now:
- Backup Google Drive to your desktop:
cp -rv /gdrive/<username> /home - "Mount" multiple Google Drive and Dropbox accounts, copy files from anywhere to anywhere.
- Plot your friends' locations on a map:
map /facebook/friends/* scrape_web_page | extract_table | draw_chart
Installation
Simply visit http://pigshell.com and type away. Modern (~early 2014) versions of Chrome, Firefox and Safari should work fine on all desktop platforms. Mobile browsers, Internet Explorer and others are not supported at the moment.
Running the psty server on your desktop is strongly recommended.
It exposes a local directory for pigshell to use as a /home, serves as a
proxy HTTP server, and lets pigshell pipe web data through desktop Unix
utilities. Psty works only on Unix currently.
Hello, World
Click on the first example in the sidebar, or type the following at the prompt:
cat http://pigshell.com/sample/life-expectancy.html | table2js -e "table.wikitable tr" foo country data | iframe -g /usr/share/template/d3-worldmap1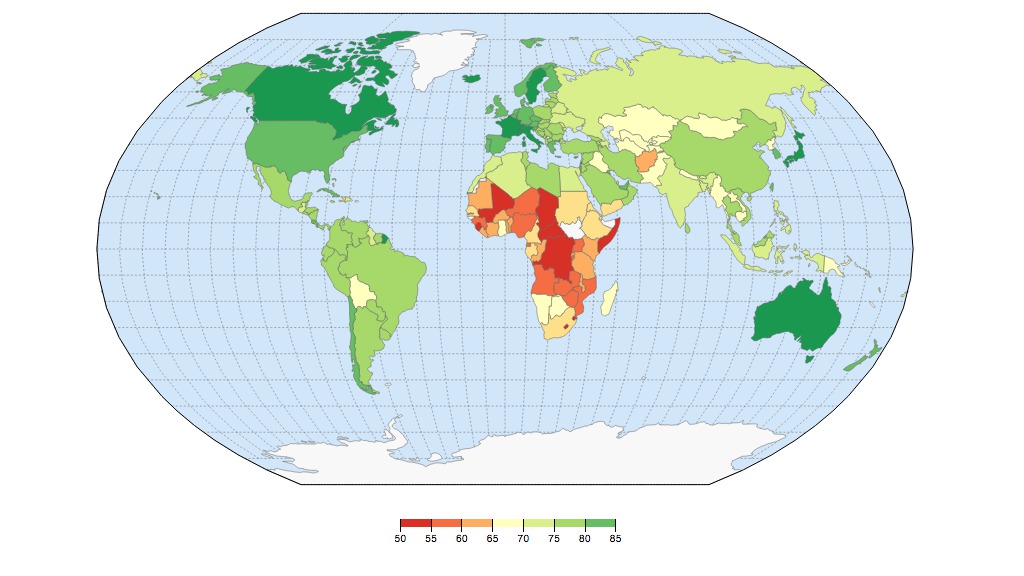
We got a page from a website, extracted a table, converted it to a list of Javascript objects and fed it to a D3-based template for visualization.
A pigshell pipeline lazily processes streams of objects. Commands should be
considered as generator functions yielding objects, composed using the pipe
operator. The pipeline starts when the last member (an implicit Stdout) asks
the upstream command for an object, which in turn asks its upstream command and
so on, until the command at the head reluctantly yields an object. It is
processed and "returned" downstream, until it hits Stdout which displays it
on the terminal. Stdout has an insatiable appetite for objects, so it asks
for one more, and the process continues until a null object, signifying the
end of the pipeline, makes its way down. Unlike Unix commands, pigshell
commands are not independently executing processes.
Using the Terminal
The terminal should be familiar to Unix/bash users, featuring tab completion, history, and Emacs-style CLI editing shortcuts.
The primary prompt is pig<basename_of_cwd>$. When a command is running,
a secondary prompt of > is displayed, which can be used to typeahead
commands.
Ctrl-C and Ctrl-Z kill and pause the current foreground command
respectively, while Ctrl-B "backgrounds" it (roughly like an Ctrl-Z +
bg in bash).
A command sequence (e.g. ls|sum; sleep 10; echo done) issued on the CLI will
fill its output area as and when objects are emitted. The prompt associated
with a command sequence glows green or amber while it is running or stopped,
and on its completion settles to red or black depending on its exit status.
Basic commands
ls, cd, mount, cat work similarly enough to their Unix namesakes to
help you explore the system.
The ps command displays a list of running pipelines. To kill a long-running
pipeline, use ps to find its PID and kill. You can also stop and start
pipelines.
Attaching Data Sources
To attach Google Drive, Picasa, Dropbox, Facebook, click on the corresponding
icon under Data Source in the sidebar. Attaching an account automatically
mounts associated filesystems under /gdrive, /picasa, /dropbox and
/facebook respectively.
Data privacy is assured: pigshell is a pure Javascript app, and data flow happens directly between your browser and data sources like Google and Facebook. No access tokens or user data are ever visible to or stored by the pigshell.com server.
Running the mount command without arguments displays the list of currently
mounted filesystems.
Everything is a file. Friends are files too. After attaching your Facebook account,
cd /facebook/friends; lswill give you a list of your friends.
Where in the world are my friends?
map /facebook/friends/*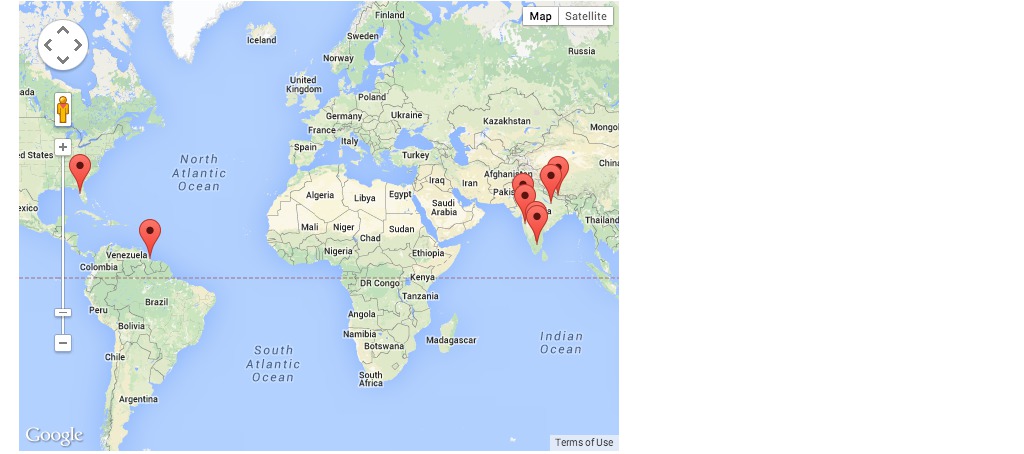
map is a command which plots files with location attributes on a map.
Another way of doing this would be
ls /facebook/friends/ | mapPigshell passes objects over pipes. In this case, ls emits a stream of
file objects, which are consumed by map.
Let's refine the above query: Where are all my male friends?
ls /facebook/friends | grep -f gender "^male" | mapgrep is a generic filter command, which may filter either by an object's text representation, or a specific field - in this case, gender.
How many friends do I have?
ls /facebook/friends | sumPie chart of relationship status of all female friends
ls /facebook/friends | grep -f gender "female" | chart -t pie -o field=relationship_status$HOME sweet $HOME
Get a /home. Download Psty, run it on your desktop:
python psty.py -a -d /some/dir # Run in DESKTOP SHELL (bash), not pigshelland on pigshell,
mount http://localhost:50937/ /home # Run in PIGSHELL, not desktopThe psty server runs only on Linux and Mac OS at present.
Now you can read and write to /home it will be backed by /some/directory.
cat images and PDFs stored on your desktop inside /some/directory.
This mount command needs to be typed every time you start or reload the page. To do it automatically,
echo "HOME=/home; mount http://localhost:50937/ $HOME" >/local/rc.sh/local/rc.sh is a script stored in the browser's LocalStorage and will be invoked every time http://pigshell.com is (re)loaded. You need to create a /local/rc.sh on every browser on which you use pigshell.
Data Movement
Assuming you're running psty, backing up Google Drive to your desktop is as simple as
mkdir /home/drivebackup
cp -rv -X /Trash /gdrive/username@gmail.com /home/drivebackupMore details on using Google Drive with pigshell.
Backing up a Picasa album:
mkdir /home/foo; cp /picasa/foo/* /home/fooSimilarly, creating an album and uploading a bunch of pictures to Picasa:
mkdir /picasa/bar; cp /home/barpics/*JPG /picasa/bar(note that album creation and uploads to Picasa require psty's proxy services)
Copying random URLs to your desktop also works:
cp -c http://ftp.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD/ISO-IMAGES-amd64/10.0/FreeBSD-10.0-RELEASE-amd64-bootonly.iso /homeThe -c option continues where it left off, so you can resume interrupted
downloads.
If you don't have psty:
You can copy the files to
/downloads, and it will get to your browser's default download folder. Note that you cannot see anything inside the/downloadsdirectory, it's just a pseudo-target to trigger a browser download. For example,cp /picasa/foo/DSC_1290.JPG /downloadsClick on Upload Files and select a file or files from your desktop. These files are now visible under the directory
/uploads. Uselsto verify that they're there. Now usecpto copy them to the target directory.cp /uploads/cat.jpg /gdrive cp /uploads/cat.jpg /facebook/me/albums/MyCat/
Data conversion
Most filesystem read() operations generate blobs. It is up to the consuming
command to convert incoming data into the type it likes. In the command
cat http://pigshell.com/sample/photos/bchips.jpgcat returns a blob. The terminal figures out that the blob contains PNG data,
and displays it as a canvas. Similarly,
cat http://pigshell.com/sample/clickingofcuthbert.pdfis detected as a PDF and displayed using pdf.js. In case it could not figure out the contents, it attempts to convert it to text and displays it as the usual control-character porridge (though it is mercifully silent, unlike Unix terminals)
In some cases, you have to manually convert data between stages in the pipeline. For example,
cat http://pigshell.com/sample/README.md | to text | jf 'x.split("\\n")' | sumimplements a poor man's wc: cat returns a blob, to converts it to text,
jf splits it into lines, sum counts the number of objects it gets. A cat
... | sum would have returned 1, since only one object (a blob) was presented
to sum.
URLs as files
Absolute URLs can be used in most places where a file path is expected. Mounting an HTTP URL exposes all links within that page as directories. To mount arbitrary, non-CORS-enabled URLs, you need to run psty.
mount http://pigshell.com/sample/ /mnt; cd /mnt; ls
cat oslogos.png
cat .
cat . | to textProcessing on the desktop - Wsh
Psty runs a websocket service, effectively converting every Unix utility which uses stdin/stdout into a potential member of the pigshell pipeline. For instance, if you have ImageMagick installed,
cat http://pigshell.com/sample/oslogos.png | wsh /usr/local/bin/convert -implode 1 - - | to -g blobwill grab a png file from the web, pipe it through ImageMagick on the desktop, and display the result in pigshell.
To visualize disk usage in a zoomable treemap,
wsh du /Users/foo | to -g text | iframe -g /usr/share/template/d3-du-treemap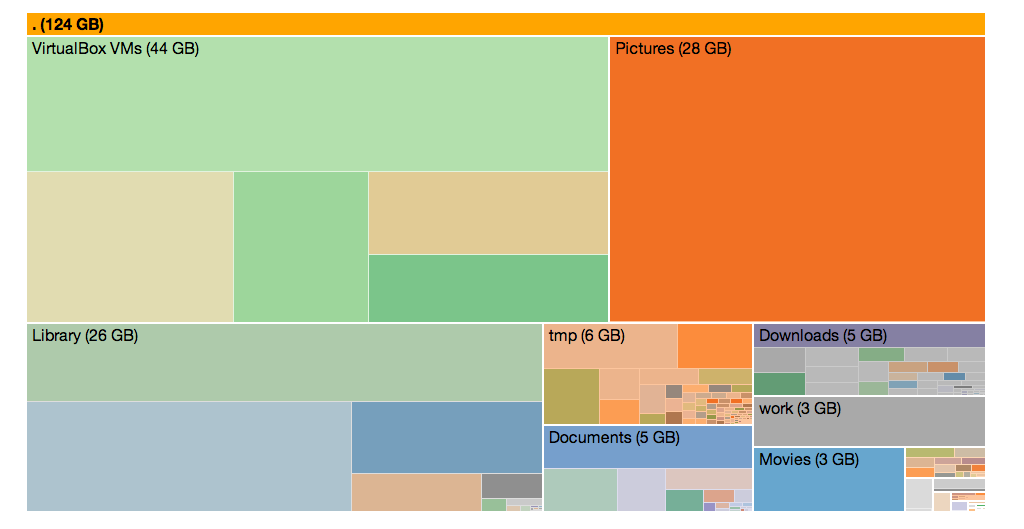
Note that du of a deep tree may take a while, try with a shallow directory
tree first)
Status
Pigshell is under active development. No commands, APIs or interfaces are frozen at this point. Tests and documentation are very sparse at the moment.
The user guide has more detailed coverage of pigshell concepts and the scripting language.
Contact
Email us at pigshell@googlegroups.com, dev@pigshell.com or follow @pigshell.
